Table of Contents
ToggleThe air content of a concrete test sample is defined as the volume of entrained air introduced into the concrete mixture during mixing, excluding the air voids contained within the aggregate particles. This air content is calculated based on the difference between the apparent air content and the aggregate correction factor, and is expressed as a percentage (%).
Equipment preparation
Type B Pressure Meter: A cylindrical container made of steel or other rigid metal, with a minimum capacity of 6 liters. The lid assembly must be airtight and equipped with an air valve, air release valve, and water valves.
Additional Tools: Rubber mallet, tamping rod, calibration tube, hand pump, and tools for mixing and placing concrete.
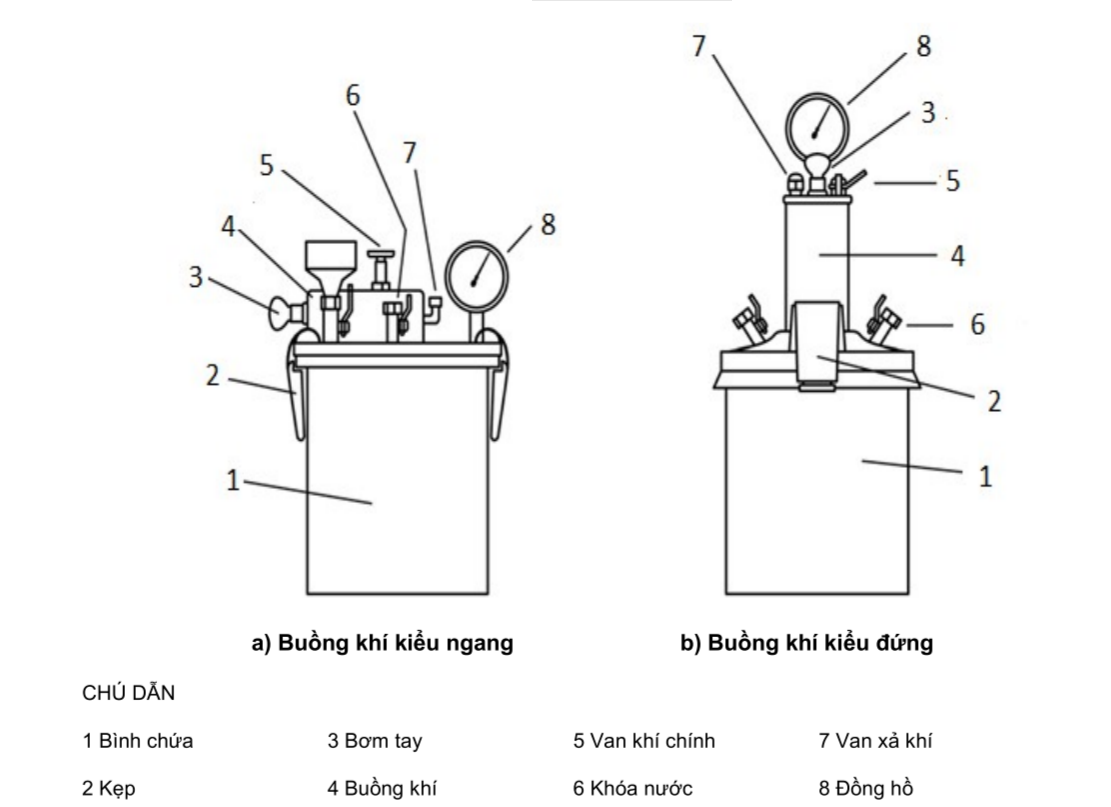
Figure 1 – Apparatus for testing air content in fresh concrete using Type B pressure meter.
Test method description (Using type B pressure meter)
This method is based on balancing a known volume of air at a predetermined pressure in a sealed chamber against the unknown volume of air in the concrete sample. The pressure gauge indicates the air content.
Work instructions
1. Preparation
Clean the rim of the container and the lid assembly to ensure airtight sealing when clamped.
Assemble the air meter, close the main air valve between the air chamber and the container, and open both water valves.
Add water through one valve until it flows out of the other. Gently shake the meter to release all air from the container.
2. Test Procedure
Close the air release valve and pump air into the chamber until the gauge reaches the initial pressure mark.
Wait a few seconds for the compressed air to cool to ambient temperature.
Stabilize the gauge needle at the initial pressure by pumping or releasing air as needed. Tap the gauge lightly with a finger to ensure stability.
Close both water valves on the lid, open the main air valve, tap the container gently with a rubber mallet, and tap the gauge to stabilize the needle.
Read the air content from the gauge and close the main air valve.
3. Completion
Pressure Release:
Gradually release pressure and open the vent to check if the water level returns to zero. Tap the container gently during this process.
Leak Check:
- If the water level does not return to zero, air may have escaped from the calibration tube or water may have leaked from the meter.
- If the water level does not return within ±0.05% of zero and no water leakage is observed, some air may have been lost from the calibration tube.
Recalibration:
If any of the above issues occur, repeat the calibration procedure from step A.6. If water leakage is detected, tighten the fittings before recalibrating.
Note: Follow all steps carefully to ensure the accuracy of the test results.
Measurement and Calculation of Results
- The air content of the concrete sample is calculated to the nearest 0.1% using the pressure meter.
- If the air content exceeds 8%, read the value closest to the nearest half division on the gauge.

Key Considerations when measuring air content in fresh concrete
When determining the air content of a concrete sample using a Type B pressure meter, the following critical points must be observed:
Sample Preparation:
The concrete sample must be prepared according to standard procedures. If necessary, ensure that no aggregate particles exceed 40 mm in size.
Equipment Calibration:
The pressure meter must be calibrated periodically—at least once every three months or whenever required. Ensure that the pressure and gauge readings are accurate.
Testing Procedure:
Ensure the internal surfaces of the lid assembly and container are clean, free of grease, and moistened to facilitate air release.
After pumping air into the chamber, allow a few seconds for the compressed air to cool to ambient temperature before taking readings.
Close the air release valve and pump air until the gauge reaches the initial pressure mark. Stabilize the gauge needle at the initial pressure by adjusting air volume as needed.
Reading the Results:
If the air content exceeds 8%, read the value closest to the nearest half division on the pressure gauge.
Permissible Error:
The difference between two consecutive test results must not exceed 0.2%. If discrepancies occur, repeat the test to ensure accuracy.
Reporting Results:
The test report must clearly state the sample name, sample ID, date and time of testing, and the measured air content of the concrete sample.
These considerations are essential to ensure the air content measurement is performed accurately and reliably.
Referrals:
- Fresh concrete – Test method for air content by the pressure method (TCVN 3111:2022)
- Standard Test Method for Air Content of Freshly Mixed Concrete by the Pressure Method (ASTM C 231 – 08c)
Từ khóa:
- air content in concrete test
- air content in concrete formula
- allowable air content in concrete
- why is air content in concrete important
- low air content in concrete
- air content test concrete procedure
- air content test for concrete pdf
- concrete air content test equipment